How Do Proteins Biological Molecules Define Antibody Specificity
Table of Contents
The immune system depends on antibodies as its main defensive proteins which achieve their specific targeting ability through multiple structural and molecular and genetic and biophysical mechanisms. Antibody specificity is fundamental to immune recognition and also underlies the principles behind many laboratory diagnostic assays and therapeutic antibody designs at the conceptual level.The precise recognition of antibodies results from their built-in structural elements and external regulatory mechanisms. The development of advanced life science tools requires knowledge about the biochemical and molecular mechanisms which control antibody specificity.
Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. operates as a leading industry player which supports researchers through their work in this field. The national high-tech enterprise Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co. Ltd. was founded in 2004. Solarbio has established itself as a worldwide life science innovation partner through its 200,000+ product and service offerings which include antibodies and recombinant proteins and ELISA kits and CRO platforms that serve more than 50 countries. The company demonstrates its dedication to quality and specificity through its complete antibody solutions which include validated Antibody products and fully customizable Custom Antibody services.
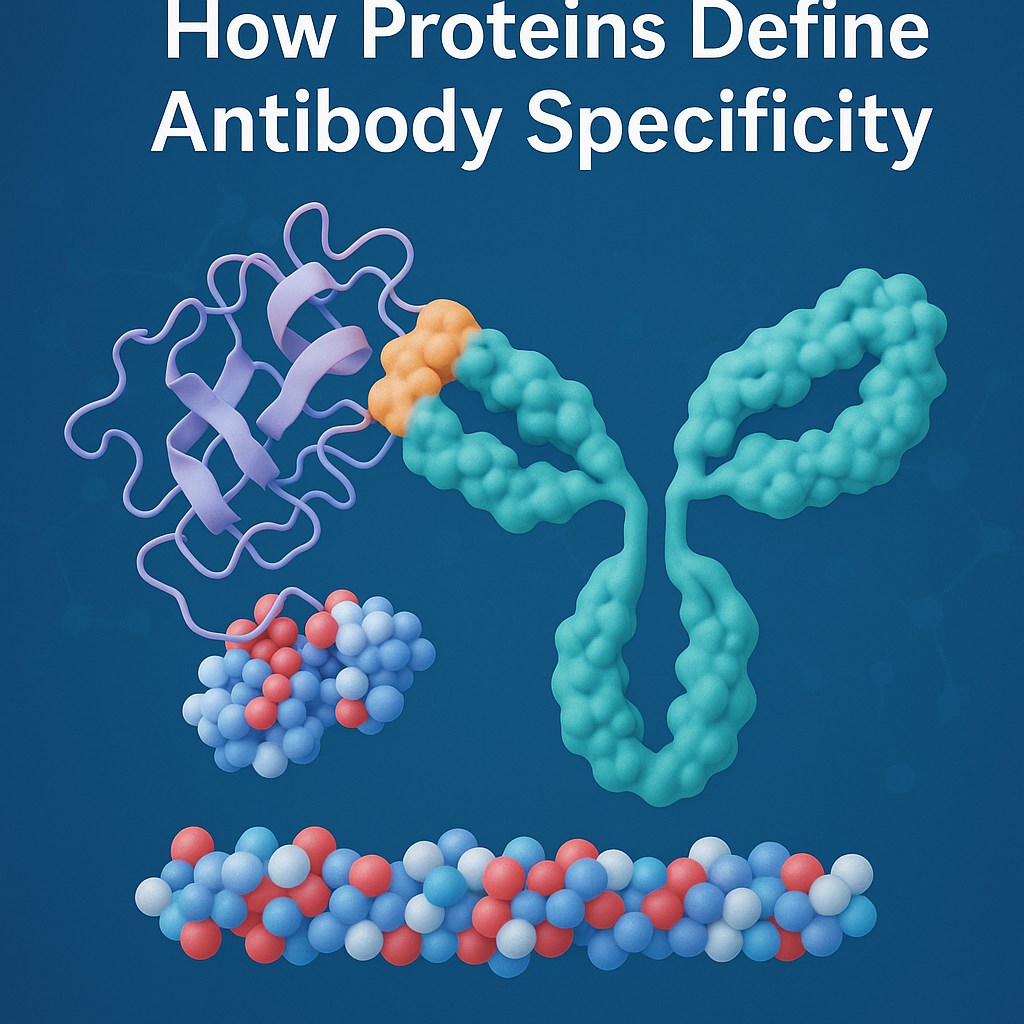
Structural Determinants of Antibody Specificity
The structure of an antibody determines which surfaces it can bind to. The variable region of the immunoglobulin molecule is crucial for antigen recognition, but specificity also involves the constant regions and the overall conformation of the antibody.

Variable Regions of Immunoglobulin Molecules
The antigen-binding site of the variable domains (VH and VL) determines specificity through their amino acid sequence diversity. The antigen-binding site of these regions consists of hypervariable loops which scientists call complementarity-determining regions (CDRs). The structural elements which recognize antigens are called Complementarity-determining regions (CDRs).
Solarbio provides monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies with optimized variable regions that enhance binding precision. The production of Solarbio antibodies follows established quality control procedures.
Role of Protein Folding and Conformational Integrity
Proper folding of the antibody ensures that the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) are positioned optimally, facilitating effective binding to epitopes, while also ensuring the overall stability and functionality of the antibody. The correct structure of CDRs depends on proper folding because it enables them to recognize antigens properly. Antibodies that fold incorrectly will either become nonfunctional or produce unintended reactions because their structural arrangement changes.
Solarbio maintains antibody production platforms which achieve structural accuracy through their strict quality control systems. The validation process for each antibody batch includes WB and IHC and IF and FCM and IP tests to confirm both structural and functional stability.
Influence of Post-Translational Modifications on Specificity
The binding strength and stability of antibody-antigen interactions can be modulated by post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, and methylation, which influence the antibody’s affinity and functional properties. The stability and binding affinity of antibodies to antigens gets influenced by glycosylation and additional modifications. The location of site-specific modifications relative to the binding site determines whether they will strengthen or break antigen binding.
Solarbio provides custom antibody services which enable researchers to add specific PTMs for enhancing antibody specificity in difficult-to-work-with applications.
Molecular Interactions Governing Antigen Recognition
The binding of antibodies to antigens occurs through multiple non-covalent interactions which determine both the binding affinity and the specificity of the interaction.
Hydrogen Bonding and Electrostatic Forces in Epitope Binding
The antibody-antigen complex achieves stability through hydrogen bonding and electrostatic forces. The molecular interface of antibody-antigen complexes remains stable through non-covalent interactions. The electrostatic attraction between CDR residues and antigens enhances the precision of antigen recognition.
Solarbio performs advanced biophysical assays to validate their antibodies for high-affinity binding. The validation process optimizes antibody performance for ELISA and flow cytometry applications because strong interaction strength is essential for these methods.
Role of Hydrophobic Interactions in Antibody-Antigen Stability
The stability of buried interfaces depends heavily on hydrophobic contacts between protein surfaces. The formation of complex structures depends on hydrophobic residues which create buried interfaces that enhance stability. The interactions function as a vital mechanism because they need to operate effectively in biological environments where ionic strength levels change.
Impact of Epitope Structure on Binding Specificity
The structure of epitopes exists in two forms which determine how antibodies detect them. The structure of linear epitopes becomes visible when proteins are denatured but conformational epitopes need their native structure to be recognized. The location of epitopes in native protein structures determines whether antibodies can bind functionally.The company Solarbio offers epitope mapping tools which help developers create antibodies that target functional domains instead of useless sequences.
Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Antibody Diversity
The specific binding properties of antibodies result from genetic changes which occur dynamically within B cells.
Somatic Recombination of Immunoglobulin Genes
The V(D)J recombination process generates diverse antigen-binding specificities by rearranging different gene segments of immunoglobulin genes in B cells. The shuffling process enables the creation of millions of distinct antibodies from a restricted number of gene segments.
Solarbio uses hybridoma and phage display platforms to tap into natural antibody diversity for creating monoclonal antibodies that target specific unique targets.
Somatic Hypermutation and Affinity Maturation Processes
The immune system chooses clones with better affinity through antigen exposure which leads to variable region mutations that accumulate at specific sites. The immune system chooses high-affinity clones through multiple rounds of antigen exposure.Solarbio uses recombinant engineering platforms to speed up reagent development for creating high-specificity reagents that perform exact functions.
Class Switch Recombination and Functional Adaptation
The specificity of antibodies stays unchanged when antibodies switch from IgM to IgG or IgA but this change affects their effector functions. The immune system distributes antibodies based on their isotype which determines their blood circulation duration and their ability to interact with immune cells.Solarbio provides researchers with isotype-specific antibody variants which they can use for research applications or therapeutic purposes.
Biophysical Properties That Define Binding Precision
The actual performance of antibodies in real-world applications depends on their thermodynamic and kinetic properties as well as their sequence and structural features.
Affinity Versus Avidity in Antibody-Antigen Interactions
The strength of single-site binding appears in Affinity measurements but avidity shows how multiple binding sites work together. Antibodies with high avidity achieve stronger binding by utilizing multiple binding sites, even if each individual site has only moderate affinity.
Thermodynamic Parameters Governing Specificity Profiles
The binding selectivity of a compound depends on both enthalpic and entropic factors. The performance of the compound depends on temperature because it affects results in different assay conditions and species models.Solarbio performs complete thermodynamic profiling to verify that their products work well in various experimental settings.
Kinetic Rates of Association and Dissociation Events
The fast on-rates of these sensors allow for quick antigen detection while their slow off-rates help maintain signal strength. The system requires specific kinetic adjustments to achieve either diagnostic accuracy or therapeutic effectiveness.
Applications Requiring High Antibody Specificity Standards
The requirement for specificity exists as a fundamental need which extends from academic studies to medical diagnosis and treatment methods and scientific research practices.
Diagnostic Assays Dependent on Minimal Cross-Reactivity
The ELISA, WB, and IHC assays can produce misleading results when off-target binding occurs. These concepts apply to research-based immunoassays.
Solarbio antibodies are validated for research applications only and are not intended for clinical diagnostic use.
Solarbio provides validated antibodies which show low off-target binding while working effectively in different assay systems.
Therapeutic Antibodies Demanding Target-Specific Safety Profiles
Therapeutic antibody design requires stringent target specificity to avoid off-target effects. The discussion here refers to principles in antibody engineering. Solarbio’s antibody products are strictly for research use only and are not for therapeutic or medical purposes.
Research Tools Supporting Mechanistic Pathway Studies
The process of dissecting cellular pathways including PI3K-AKT and TNFSF signaling requires exact tools. Solarbio offers pathway-specific antibodies which connect to signaling networks that researchers have validated. Scientists who study neurotrophin pathways and inflammasome cascades need precise molecular targeting tools to achieve their research goals.
Technological Platforms Enhancing Antibody Specificity Engineering
The development of antibodies requires technological platforms which allow researchers to select and refine their antibodies while scaling up their production.
Hybridoma Technology for Monoclonal Antibody Production
The classical method uses cell fusion to identify particular B cell clones which receive immortalized cell properties. The fusion-based selection technique enables researchers to identify and extract B cell clones that show high specificity. The method produces continuous supply of material with minimal differences between production batches.
Solarbio operates a dedicated hybridoma platform which produces both experimental batches and commercial-scale production quantities.
Recombinant Antibody Engineering Approaches
Recombinant technology allows scientists to create precise designs through sequence humanization and format changes between scFv and Fab structures. The humanization process minimizes immune reactions while maintaining the ability to recognize specific epitopes.
Solarbio provides recombinant formats which undergo testing under ISO-certified QC frameworks to fulfill research requirements at high levels.
Phage Display Libraries Enabling High-Diversity Screening
Phage display technology allows researchers to select specific binders from massive libraries which contain rare molecules that show high specificity. The selection process through multiple panning steps leads to better enrichment of desired characteristics.
The Solarbio Services platform enables users to start their custom phage display project.
Customization Strategies Tailored to Research Needs
Research challenges demand individualized answers because they present distinct problems which standard catalog solutions cannot solve.
Target-Specific Custom Antibody Generation Services
Solarbio enables users to define their own inputs throughout all stages of custom antibody development from design to validation through its complete custom antibody services.
Species-Specific Options Supporting Cross-Reactivity Control
The selection of host species in model systems determines how much background material will be present in the system. The process of cross-species reactivity screening helps scientists avoid wrong interpretations when they compare different species. Solarbio provides different species including rabbit and mouse and goat and additional options for users to optimize their specific systems.
Conjugation Services Enhancing Application Flexibility
The application of conjugates increases experimental possibilities through their use as fluorescent dyes for flow cytometry and HRP for ELISA. The process of site-directed labeling enables researchers to modify proteins while maintaining their ability to bind antigens.
FAQ
Q1: What determines the specificity of an antibody?
The variable regions VH and VL together with their CDRs determine the specificity of antibodies through their distinct amino acid sequences which create the antigen-binding site.
Q2: How does Solarbio ensure high-quality antibody production?
A: The purification process of Solarbio antibodies involves affinity chromatography which results in antibodies with high specificity and affinity. The antibodies receive validation testing for WB and IHC and IF and FCM and IP and knockout model applications.
Q3: Why is antibody validation important in diagnostic assays?
A: Validation ensures that antibodies bind to the target antigen with high specificity and stability, minimizing cross-reactivity and ensuring consistent performance across different batches in diagnostic tests like ELISA and Western blot.