B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway
Introduction
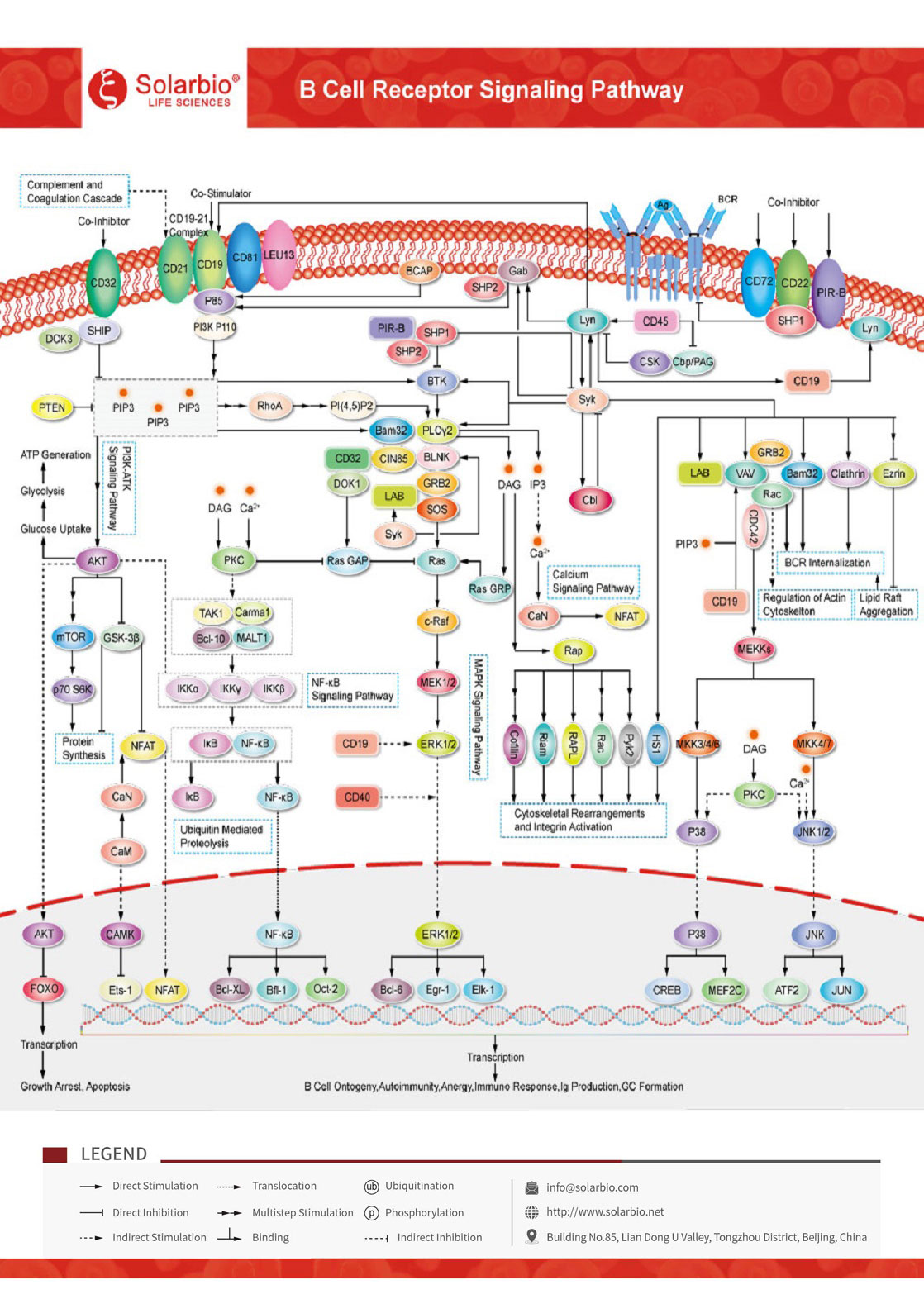
B cells are an important part of adaptive immunity. They produce and secrete millions of different antibody molecules, each recognizing a different (foreign) antigen. The B-cell receptor (BCR) is an integral membrane protein complex consisting of a cell membrane immunoglobulin (mIg) molecule and an associated Igα/Igβ heterodimer (α/β). After antigen ligation of the BCR, several major protein tyrosine kinases (PTKS), including SRC family kinase member proteins (LYN, BLK, FYN), TEC family kinases (BTK), and SYK family kinases (SYK), are activated in turn. Direct downstream effectors of SYK phosphorylation include VAV1, PLCG1, PI3K, LCP2, and BLNK. PI3K and PLC-γ2 are important downstream effectors of BCR signaling. The cascade of amplified signals ultimately leads to the expression of immediate early genes, which further activate changes involved in B-cell proliferation, differentiation and Ig production, cell metabolism, gene expression, and cytoskeletal architecture.