T Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway
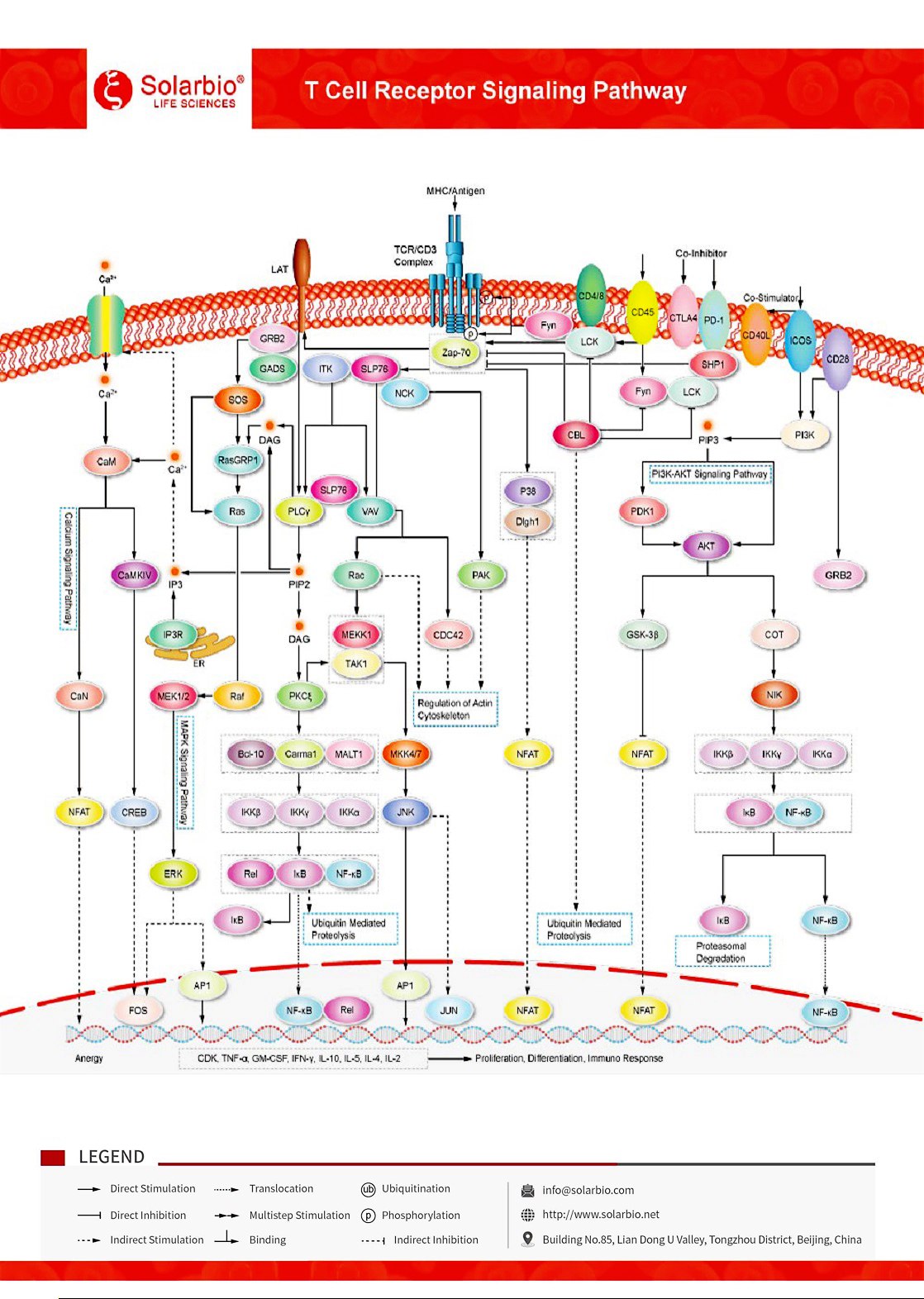
TCR (T cell receptor) is a characteristic marker on the surface of all T cells, which binds to CD3 by non-covalent bond to form TCR-CD3 complex. TCR is a heterodimer composed of two different peptide chains, α and β. The TCR-CD3 complex consists of genetically diverse αβ (or γδ) TCR heterodimers that are noncovalently bound to invariant CD3 dimers: CD3ϵγ, CD3ϵδ, and CD3ζζ. The TCR mediates the recognition of peptide fragments that bind to major histocompatibility complex molecules on antigen-presenting cells. Its activation can promote many signal transduction cascades. The early event of TCR activation is the phosphorylation of immune-receptor tyrosine-dependent activation motifs (ITAMs) on the cytoplasmic side of the TCR/CD3 complex by lymphocyte protein tyrosine kinases (Lck), which contain one immune-receptor tyrosine-dependent activation motif (ITams) for CD3ϵ, γ, δ and three immune-receptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITams) for the ζ chain. When phosphorylated by the Src kinase Lck, these motifs initiate a downstream T-cell signaling cascade. Tyrosine phosphatases of the CD45 receptor regulate the phosphorylation and activation of Lck and other Src family tyrosine kinases. Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase (Zap-70) is recruited, aggregated and activated at the TCR/CD3 complex, which initiates the recruitment and phosphorylation of downstream adaptor or backbone proteins. When phosphorylated by Zap-70, SLP-76 promotes the recruitment of Vav (a guanylate exchange factor), the adaptor proteins NCK and GADS, and an inducible T-cell kinase (Itk). Phosphorylation of phospholipase Cγ1(PLCγ1) by LTK results in the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-diphosphate (PIP2) to produce the second messengers diglyceride (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3). DAG activates PKCθ and MAPK/Erk pathways, both of which promote the activity of the transcription factor NF-κB. IP3 triggers Ca2+ release from the ER and promotes extracellular Ca2+ entry into the cell via Ca2+ release activated Ca2+(CRAC) channels. Ca2+ binding calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) activates calcineurin, which promotes IL-2 gene transcription through the transcription factor NFAT. Since several studies have shown that the T cell costimulation/coinhibition system can be used to enhance antitumor immunity, many molecules of these proteins are being investigated as potential targets for cancer immunotherapy.