Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily (TNFSF)
Classification
Human TNF Superfamily Ligands and Their Expression Profiles
|
Official Name |
Ligand |
Expressing Cells |
|
TNFSF1 |
TNF-β,LT-a |
NK cells, T cells, B cells |
|
TNFSF2 |
TNF-α |
Macrophages, NK cells, T cells, B cells |
|
TNFSF3 |
LT-β |
Activated CD4⁺ T cells, T cells, Dendritic cells (DCs), NK cells |
|
TNFSF4 |
OX40L(CD252) |
B cells, T cells, DCs, Endothelial cells, Smooth muscle cells |
|
TNFSF5 |
CD40L(CD154) |
Activated CD4⁺ T cells, Mast cells, Basophils, Eosinophils, NK cells |
|
TNFSF6 |
FasL(CD95L,Apo1L) |
Activated splenocytes, Thymocytes, Non-lymphoid tissues, NK cells |
|
TNFSF7 |
CD27L(CD70) |
NK cells, T cells, B cells, Mast cells, Smooth muscle cells, Thymic epithelial cells |
|
TNFSF8 |
CD30L(CD153) |
Activated T cells, B cells, Monocytes, Granulocytes, Medullary thymic epithelial cells |
|
TNFSF9 |
4-1BBL |
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs: B cells, DCs, Macrophages), Mast cells |
|
TNFSF10 |
TRAIL(Apo2L) |
DCs, NK cells, T cells |
|
TNFSF11 |
RANKL(TRANCE,OPGL,ODF) |
T cells, Thymus, Lymph nodes |
|
TNFSF12 |
TWEAK(Apo3L) |
Monocytes |
|
TNFSF12-TNFSF13 |
TWE-PRIL |
Renal tubular epithelial cells |
|
TNFSF13 |
APRIL(TALL-2,TRDL-1) |
Macrophages, Lymphocytes, Tumor cells |
|
TNFSF13B |
BAFF |
Monocytes, Macrophages |
|
TNFSF14 |
LIGHT,CD258 |
Lymphocytes |
|
TNFSF15 |
TL1A |
Endothelial cells |
|
TNFSF18 |
GITRL,TL6 |
Endothelial cells |
|
Official Name |
Receptor |
Expressing Cells |
|
TNFRSF1A |
TNFR1(DR1) |
Hematopoietic and immune cells |
|
TNFRSF1B |
TNFR2 |
Immune and endothelial cells |
|
TNFRSF3 |
LT-BR |
NK cells, CD4⁺ and CD8⁺ T cells |
|
TNFRSF4 |
OX40(CD134) |
Activated CD4⁺ T cells, Neutrophils |
|
TNFRSF5 |
CD40 |
B cells, Dendritic cells (DCs), Monocytes, Thymic epithelial cells, Reed–Sternberg cells |
|
TNFRSF6 |
Fas(CD95,Apol,DR2) |
Epithelial cells, Hepatocytes, Activated mature lymphocytes, Transformed cells |
|
TNFRSF6B |
DcR3 |
Pulmonary and colonic epithelial cells |
|
TNFRSF7 |
CD27 |
Hematopoietic progenitor cells, CD4⁺ and CD8⁺ T cells |
|
TNFRSF8 |
CD30 |
Reed–Sternberg cells |
|
TNFRSF9 |
4-1BB(CD137,ILA) |
T cells, NK cells, Mast cells, Neutrophils |
|
TNFRSF10A |
TRAILR1(DR4,Apo2) |
Most normal and transformed cells |
|
TNFRSF10B |
TRAILR2(DR5) |
Most normal and transformed cells |
|
TNFRSF10C |
TRAILR3(DcR1) |
Most normal and transformed cells |
|
TNFRSF10D |
TRAILR3(DcR2) |
Most normal and transformed cells |
|
TNFRSF11A |
RANK(TRANCER) |
Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts, Activated T cells |
|
TNFRSF11B |
OPG(OCIF) |
Osteoclast precursors, Endothelial cells, etc. |
|
TNFRSF12A |
TWEAKR(FN14) |
Endothelial cells, Fibroblasts |
|
TNFRSF13A/17 |
BCMA |
B cells, PBLs, Spleen, Thymus, Lymph nodes, Liver, Adrenal glands |
|
TNFRSF13B |
TACI |
B cells, Activated T cells, PBLs, Spleen, Thymus, Small intestine |
|
TNFRSF13C |
CD268,BAFFR |
B lymphocytes |
|
TNFRSF14 |
CD270,LIGHTR |
T cells, Intestinal epithelial cells |
|
TNFRSF16 |
NGFR |
Various types of stem cells |
|
TNFRSF18 |
GITR |
T cells |
|
TNFRSF19 |
TRADE |
Peripheral blood leukocytes |
|
TNFRSF19L |
TRLT |
Peripheral blood leukocytes, Spleen, Lymph nodes |
|
TNFRSF21 |
DR6 |
Cerebrospinal fluid cells |
|
TNFRSF25 |
DR3 |
Adipocytes |
|
TNFRSF27 |
XEDAR |
Embryonic hair follicles |
|
EDAR |
EDAR |
Ectoderm-associated cells |
Regulatory Mechanisms
Currently, the 29 receptors of the TNF receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) can be categorized into three major groups:
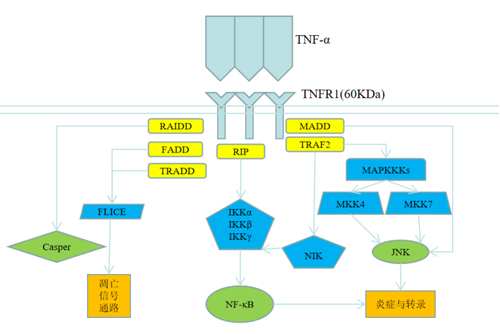
The first group consists of receptors that contain a death domain (DD) in their cytoplasmic tail. Upon ligand binding, these receptors recruit intracellular adaptor proteins with DDs to form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC), leading to caspase activation and the induction of apoptosis.
The second type of receptors contain one or more TRAF interaction motifs (TIMs) in the cytoplasmic domain. Activation of these receptors directly recruits members of the TRAF family, ultimately leading to the activation of key signaling pathways involved in cell survival, proliferation, and inflammation.
The third group comprises receptors lack functional intracellular signaling domains or motifs. Although these “decoy” receptors do not initiate intracellular signaling, they can competitively bind to ligands, thereby modulating the signaling of the first two groups by preventing ligand-receptor interactions
Related Products
If you want to get more details, please go to our Store website: www.solarbio.com.
|
Cat No. |
Product Name |
Cat No. |
Product Name |
|
SEKH-0047 |
Human TNF-α ELISA Kit |
SEKH-0128 |
Human CD258/LIGHT/TNFSF14 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKH-0048 |
Human TNF-β ELISA Kit |
SEKH-0192 |
Human GITR/TNFRSF18 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKH-0126 |
Human TNFRSF9/CD137/4-1BB ELISA Kit |
SEKH-0204 |
Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKH-0313 |
Human TNF RI/TNFRSF1A ELISA Kit |
SEKH-0314 |
Human sTNF RII/TNFRSF1B ELISA Kit |
|
SEKH-0327 |
Human TRAIL/TNFSF10 ELISA Kit |
SEKH-0335 |
Human TWEAK/TNFSF12 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKM-0137 |
Mouse TRAIL/TNFSF10 ELISA Kit |
SEKM-0034 |
Mouse TNF-α ELISA Kit |
|
SEKM-0215 |
Mouse Pentraxin 3/TSG-14 ELISA Kit |
SEKM-0207 |
Mouse TNFR2/TNFRSF1B ELISA Kit |
|
SEKM-0245 |
Mouse TNFRSF1A ELISA Kit |
SEKM-0225 |
Mouse LIGHT/TNFSF14 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKM-0304 |
Mouse 4-1BB/TNFRSF9 ELISA Kit |
SEKM-0303 |
Mouse GITR/TNFRSF18 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKM-0317 |
Mouse TNFRSF19/YROY ELISA Kit |
SEKM-0307 |
Mouse TL1A/TNFSF15 ELISA Kit |
|
SEKS-0003 |
Sheep TNF-a ELISA Kit |
SEKR-0009 |
Rat TNF-α ELISA Kit |
|
SEKP-0009 |
Porcine TNF-α ELISA Kit |
SEKMY-0001 |
Monkey TNFα ELISA Kit |
|
SEKRT-0402 |
Rabbit TNF-α ELISA Kit |
SEKB-0303 |
Bovine TNF-α ELISA Kit |
|
SEKF-0145 |
Feline TNF-α ELISA Kit |
SEKC-0033 |
Canine TNF-α ELISA Kit |
|
SEKG-0001 |
Guinea Pig TNFa ELISA Kit |
SEKCN-0006 |
Chicken TNF-α ELISA Kit |